Information on Jet Lag

With more and more people travelling long distances today, a remedy for jet lag has never been more necessary. The global tourism market has grown to huge proportions, business and social travel has been redefined with vast technological advancement in which the ease of booking, traveling and experiencing a journey is beyond simple. Travel spending, hotels, booking sites and destination marketing organizations are adapting to this incredible leap towards a world that is so much more accessible than ever before. Jet lag can be debilitating, with symptoms that can ruin vacations, sabotage business trips or simply wreak havoc on our general health.
There are several things that can be done to combat this condition, with a better understanding of the causes and how to address the symptoms, we can combat jet lag and ensure a superior travel experience.
What is Jet Lag?
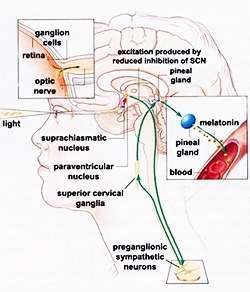
Circadian rhythms refer to our body's natural 24-hour sleep/wake cycle, where physical, mental and behavioral changes occur dependent upon & responding to - light and dark stimuli. Jet lag, also referred to as desynchronosis or circadian dysrythmia, is a physiological condition that stems from changes in the body's circadian rhythms from fast long distance travel on high-speed aircraft. Years ago, jet lag was not an issue, only with the evolvement of the passenger jet aircraft, and the ability to travel further and faster, did jet lag become a recognized condition.
Jet lag is a chronobiological condition, that occurs when traveling across a number of time zones. It renders the body's balance (circadian rhythm) out of synchronization. It experiences light/dark in contrast to the rhythms it is used to, upsetting the body's natural balance, so the rhythms that affect eating, sleeping, hormonal regulations, etc. become confused so they no longer correspond to the environment. In addition, they are unable to immediately rectify this quickly and as such the body experiences the symptoms we refer to as jet lag.
Anyone can suffer from jet lag. The direction of travel, distance and each individual will experience jet lag differently.
Jet Lag Symptoms

Symptoms vary from person to person based on the amount of time zone difference, time of day and each individual's health. The most commonly experienced symptoms are sleep disturbances, extreme tiredness, cognitive effects including lowered concentration, headaches and irritability. Additionally, changes in appetite and digestive issues can also occur.
In general, it is suggested that a change of three time zones or more will increase the chances of jet lag occurring, albeit some individuals can be affected by crossing only one time zone. It is thought that a recovery rate of one day per time zone crossed is sufficient for over coming jet lag. If only one time zone has been crossed, some feel that after a day and a good night's sleep, the body should be re-balanced.
There has been a lot of research directed towards athletes and travel, and how jet lag can affect their performance. Physical and mental characteristics can be drastically affected, so a specific measurement scale was devised, called the Liverpool Jet Lag Questionnaire, to ascertain symptoms of jet lag and assess the impact upon their performance in competitions. This provides useful insight into a condition that can affect so many.
Being aware of how jet lag occurs and the effective ways in which we can manage symptoms will help us reduce jet lag and enhance our travel experience like never before.
What are the Causes and Characteristics of Jet Lag?
Many travelers can experience general travel fatigue, which can include symptoms of general tiredness, headache and disorientation. The impact of these symptoms soon disappear once our bodies are re-hydrated effectively and have had a good night's sleep.
However, when we cross multiple time zones, it is not simply travel fatigue but jet lag that we experience. Travelling west-east and east-west (trans-meridian) is more likely to cause jet lag, travelling north-south generally does not present symptoms of jet lag as time zones are not crossed. Generally, travelling east to west travel presents less jet lag symptoms than west to east. This is fundamentally due to the fact that our body clock has to be moved forward, which is more difficult than delaying it. The further we travel, the worse symptoms may present.
It is thought that travelling west results in fewer problems and exposure to light during the day and avoiding it during the night is sufficient to overcome jet lag.
How to Prevent Jet Lag?
Light is one of the strongest regulators for re-aligning sleep-wake schedule, so careful exposure/avoidance of bright lights can speed up adjustment. There is also evidence that melatonin may help reduce jet lag, however, there remains issues regarding the appropriate timing of melatonin use with certain studies actually demonstrating that it has no benefit at all. Its effectiveness is questionable and for certain groups, such as athletes, may even be illegal.
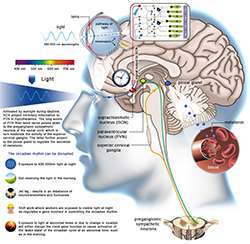 There are many basic steps that you should take to reduce the symptoms of jet lag, even starting days prior before you even fly. Some airlines actually provide jet lag calculators and programs detailing the most effective steps to take to reduce symptoms.
There are many basic steps that you should take to reduce the symptoms of jet lag, even starting days prior before you even fly. Some airlines actually provide jet lag calculators and programs detailing the most effective steps to take to reduce symptoms.
Altering sleep patterns prior to departure, diet and exercise, sleep/stimulating substances, remaining re-hydrated during the flight and sleeping on the plane can all assist in regulating your body clock to avoid the symptoms of jet lag.
References:
1 - The Lancet - Jet Lag Trends and Coping Strategies







 Jet Relief™'s formulation of effective ingredients and strong name recognition have brought praise from both customers and health professionals alike. To learn more about the research and data behind Jet Relief™ , please visit our "
Jet Relief™'s formulation of effective ingredients and strong name recognition have brought praise from both customers and health professionals alike. To learn more about the research and data behind Jet Relief™ , please visit our "




